Table Of Content
This design is particularly useful in health and social care research. For instance, if a hospital wants to implement a new hygiene protocol, it might start in one department, assess its impact, and then roll it out to other departments over time. This allows the hospital to adjust and refine the new protocol based on real-world data before it's fully implemented. Let's now focus on the Stepped Wedge Design, a thoughtful and cautious member of the experimental design family. Next up is the Solomon Four-Group Design, the "chess master" of our research team. Named after Richard L. Solomon who introduced it in the 1940s, this method tries to correct some of the weaknesses in simpler designs, like the Pretest-Posttest Design.
Creating Factorial DOE
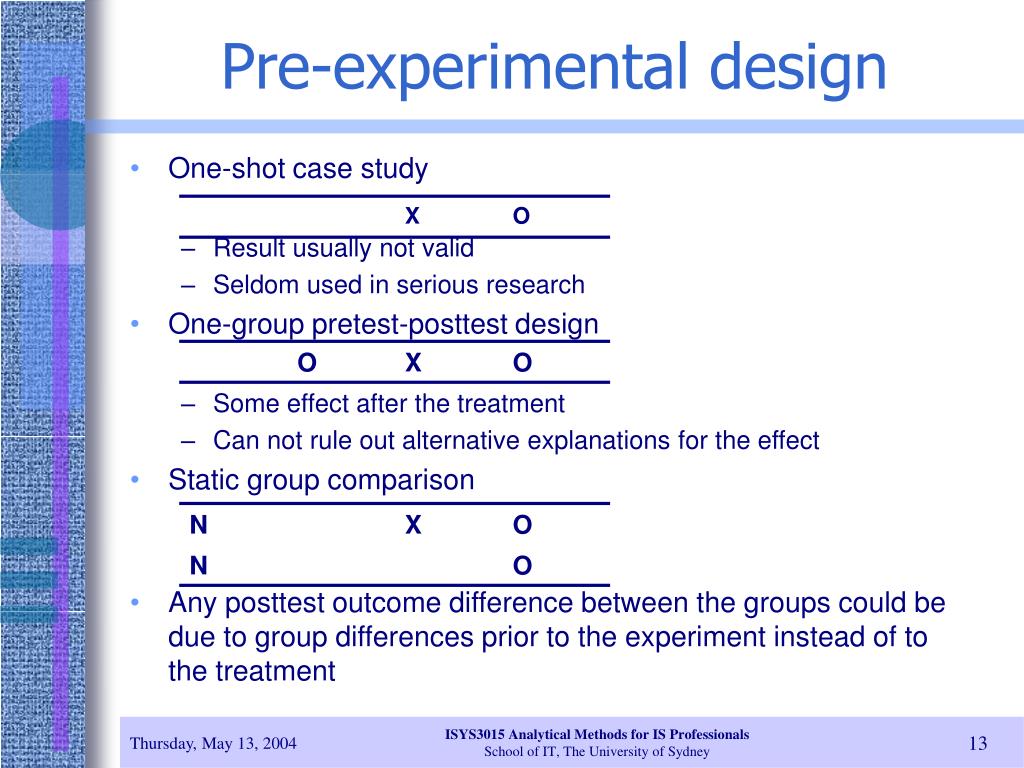
Pre-experimental designs are great for quick-and-dirty research when you're short on time or resources. They give you a rough idea of what's happening, which you can use to plan more detailed studies later. Pre-Experimental Designs are the basic, no-frills versions of experiments. Researchers still mess around with an independent variable and measure a dependent variable, but they skip over the whole randomization thing and often don't even have a control group. Similarly, pre-experimental designs give researchers a starting point.
Step 1: Define variables and their relationship
What Is a Longitudinal Study? - Verywell Mind
What Is a Longitudinal Study?.
Posted: Sat, 02 Dec 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
However, they require a great deal of expertise and careful planning to ensure that the adaptability doesn't compromise the integrity of the research. Now, let's talk about Adaptive Designs, the chameleons of the experimental world. One famous use of Pretest-Posttest Design is in evaluating the effectiveness of driver's education courses. Researchers will measure people's driving skills before and after the course to see if they've improved. Let's say you're a teacher and you want to know if a new math program helps kids get better at multiplication.
Types of experimental research designs
From this information, you can conclude that the chance of a patient suffering a seizure is minimized at lower dosages of the drug (5 mg). Both of these graphs only contain one main effect, since only dose has an effect the percentage of seizures. Whereas, graphs three and four have two main effects, since dose and age both have an effect on the percentage of seizures. For many designed studies, the sample size is an integer multiple of the total number of treatments. This integer is the number of times each treatment being repeated and one complete repitition of all treatments (under similar experimental conditions) is called a complete replicate of the experiment.
The sign of the number also has a direct correlation to the effect being positive or negative. The experiment should be conducted a number of times to insure that the results are real. In addition, within an experiment there should be an appropriate number of replications. An experiment designed to investigate the effects of fertilizer on plants would use many plants in each group.

The research design is categorized into three types based on the way you should conduct the research. Each type has its own procedure and guidelines, which you should be aware of to achieve reliable data. The main idea is to ensure the presence of different sets of variables to study with some shared commonality. Suppose a group of 300 people volunteer for a study involving office workers in their 20s. From this one can see that there is an interaction effect since the lines cross. One cannot discuss the results without speaking about both the type of fertilizer and the amount of water used.
The next step is selecting which terms will be analyzed for the responses. After the number of factors is chosen, click on the "Designs..." option to see the following menu. The issue of measurement bias arises due to unrecognizable differences in the evaluation process. In an investigation of the effects of education on income, the factor being studied is education level (qualitative but ordinal). This procedure uses mathematical, physical, or computer models to replicate a real-life process or situation. It is frequently used when the actual situation is too expensive, dangerous, or impractical to replicate in real life.
In 1950, Gertrude Mary Cox and William Gemmell Cochran published the book Experimental Designs, which became the major reference work on the design of experiments for statisticians for years afterwards. Video recording involves recording participants’ behavior or interactions using cameras or other recording equipment. This method can be used to capture detailed information about participants’ behavior or to analyze social interactions. Self-report measures involve asking participants to report their thoughts, feelings, or behaviors using questionnaires, surveys, or interviews. In your research design, it’s important to identify potential confounding variables and plan how you will reduce their impact. Some variables, like temperature, can be objectively measured with scientific instruments.
So there you have it—a quick tour through the history of experimental design, from Aristotle's deep thoughts to Fisher's groundbreaking ideas, and all the way to today's computer-powered research. These designs are the recipes that help people from all walks of life find answers to their big questions. The classification of the research subjects, conditions, or groups determines the type of research design to be used. Participants are randomly assigned to either receive the medication or nothing at all. Three months later, all participants are contacted and they are given a full battery of heart disease tests. To narrow the field of view, a random selection of individuals from the population is carried out.
It is used to make predictions and draw conclusions on a subject matter. The choice of setting used in research depends on the nature of the experiment being carried out. Let us consider an academic institution that wants to evaluate the teaching method of 2 teachers to determine which is best. Imagine a case whereby the students assigned to each teacher is carefully selected probably due to personal request by parents or due to stubbornness and smartness.
It wants to be just like its famous relative, but it's a bit more laid-back and flexible. You'll find quasi-experimental designs when it's tricky to set up a full-blown True Experimental Design with all the bells and whistles. Also, did you know that experimental designs aren't just for scientists in labs? They're used by people in all sorts of jobs, like marketing, education, and even video game design! Yes, someone probably ran an experiment to figure out what makes a game super fun to play.
This is a pretest-posttest control group experimental research example. Experimental research is the most familiar type of research design for individuals in the physical sciences and a host of other fields. This is mainly because experimental research is a classical scientific experiment, similar to those performed in high school science classes. All this means is that we wish to determine the effect an independent explanatory variable has on a dependent response variable.
In other cases, the goal is to find the level of the factors that optimizes the response, in which case a design that produces more precise predictions is better. The I-criterion, which minimizes the average prediction variance across the design region, is a natural choice. This guide explores the types of experimental design, the steps in designing an experiment, and the advantages and limitations of experimental design. When testing a theory or new product, it can be helpful to have a certain level of control and manipulate variables to discover different outcomes. You can use these experiments to determine cause and effect or study variable associations.
The group that receives the experimental treatment is the experimental group. For example, if the effect of aspirin on heart disease is being investigated, the experimental group is the group of individuals taking aspirin. For example, one group may take a pill containing no aspirin, another group consumes one aspirin a day, while a third group may take 2 aspirins a day. This method is commonly used in engineering and operational research for learning purposes and sometimes as a tool to estimate possible outcomes of real research. Experimental research design can be majorly used in physical sciences, social sciences, education, and psychology.
As seen in the above plots, RPM has significant effects for both responses and pressure has a statistically significant effect on wt% methanol in biodiesel. Neither flow rate or ratio have statistically significant effects on either response. The Pareto charts are bar charts which allow users to easily see which factors have significant effects. Because experiments from the POD are time consuming, a half fraction design of 8 trial was used. Factors A - D can be renamed to represent the actual factors of the system.
No comments:
Post a Comment